Continuing the Lesser Known series, this fourth article of the series will let you know some useful funny and animated commands. Here we go into the practical session, without much theory.

- 11 Lesser Known Useful Linux Commands – Part I
- 10 Lesser Known Linux Commands – Part 2
- 10 Lesser Known Commands for Linux – Part 3
- 10 Lesser Known Useful Linux Commands- Part V
In the fourth article of this series which includes few other lesser known Linux commands, worth knowing. Might be you’re already aware of these commands, no doubt you’re an experienced Linux user and loves exploration.
32. strace Command
The strace is a debugging tool which is used primarily for troubleshooting purpose in Linux. It might not be installed by default in your system and you may need to apt or yum the required package.
Trace a command execution using strace command:
root@tecmint [~]# strace pwd
Sample Output
execve("/bin/pwd", ["pwd"], [/* 29 vars */]) = 0
brk(0) = 0x728000
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f29b0df2000
access("/etc/ld.so.preload", R_OK) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
open("/etc/ld.so.cache", O_RDONLY) = 3
fstat(3, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0644, st_size=38427, ...}) = 0
mmap(NULL, 38427, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, 3, 0) = 0x7f29b0de8000
close(3) = 0
open("/lib64/libc.so.6", O_RDONLY) = 3
read(3, "\177ELF\2\1\1\3\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\3\0>\0\1\0\0\0\360\355\1I;\0\0\0"..., 832) = 832
fstat(3, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0755, st_size=1922152, ...}) = 0
mmap(0x3b49000000, 3745960, PROT_READ|PROT_EXEC, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0) = 0x3b49000000
mprotect(0x3b4918a000, 2093056, PROT_NONE) = 0
mmap(0x3b49389000, 20480, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0x189000) = 0x3b49389000
mmap(0x3b4938e000, 18600, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x3b4938e000
close(3) = 0
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f29b0de7000
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f29b0de6000
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f29b0de5000
....
The strace command accepts a lot of arguments and have many options. Refer to man page for detailed information.
33. disown -a && exit Command
Most of the system administrators use screen command to control jobs running in the terminal background. Let’s say if you having a long running job and want to detach from the terminal, you use screen command to do it. But what if you don’t know how to use screen, here comes disown command to rescue.
The disown command is used to run the jobs continuously in the background even after you closing the terminal session. The syntax of the disown command is:
root@tecmint [~]# Command; disown -a && exit
To detach again the long running job in the terminal, use the jobs command to find the job number and then use disown %n where n is the job number. To verify actually the job is running use ps or top command. The nohup command is an alternative to the disown command.
34. getconf LONG_BIT Command
The above command shows your machine architecture if it is 32 bit or 64 bit?
root@tecmint [~]# getconf LONG_BIT 32
Download Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet

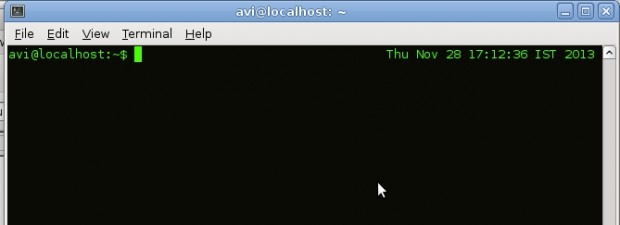
35. Display Date on the Terminal
The below command is a combination of several commands, better say it a script. For a person working at shell or terminal, without GUI seeing current system date is tedious job. You have to type ‘date‘ command to check today’s date.
Just execute the below command on you prompt and see the date and time on the above right corner of terminal.
root@tecmint [~]# while sleep 1;do tput sc;tput cup 0 $(($(tput cols)-29));date;tput rc;done &
36. convert Command
While writing tutorial, I usually need to produce output, many a times in image format. The above command combination does this for me. Say I need the output of tree command (for /etc/x11 directory) in image format. What I did at terminal was:
root@tecmint:/etc/X11# tree | convert label:@- /home/avi/tree.png
The output of the above command can be seen at the specified location (here, home directory of mine) with the file name specified as tree.png.
37. watch -t -n1 “date +%T|figlet”
Remember our description of “figlet” command in our earlier article “20 Funny Commands of Linux”. This command was very cool, this time we will be pipelining ‘figlet‘ to show animated digital clock in the terminal.
Just check-out yourself, remember you must have figlet installed on the system, do apt or yum to install the required package.
root@tecmint [~]# watch -t -n1 "date +%T|figlet"
Sample Output
_ ___ ____ ___ _____ _ _ Fri Nov 29 10:29:34 GMT / |/ _ \ _|___ \ / _ \ _|___ /| || | | | | | (_) __) | (_) (_) |_ \| || |_ | | |_| |_ / __/ \__, |_ ___) |__ _| |_|\___/(_)_____| /_/(_)____/ |_|
38. host and dig Commands
Although “host” and “dig” command is not that much lesser known, still not very frequently used. The host command is DNS lookup utility.
root@tecmint [~]# host www.google.com www.google.com has address 173.194.66.147 www.google.com has address 173.194.66.105 www.google.com has address 173.194.66.99 www.google.com has address 173.194.66.104 www.google.com has address 173.194.66.106 www.google.com has address 173.194.66.103 www.google.com has IPv6 address 2a00:1450:400c:c03::68
root@tecmint [~]# dig www.google.com ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.17.rc1.el6_4.6 <<>> www.google.com ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<
39. dstat Command
The dstat is a versatile tool, that generates statistics relating to system resource. By default your system might not have ‘dstat‘ installed. Do a apt or yum to install ‘dstat‘ before using this very colorful and description system resource generator.
root@tecmint [~]# dstat

40. bind -p Command
The ‘bind -p‘ command will show all the shortcuts available for BASH shell.
root@tecmint [~]# bind -p
Sample Output
"\C-g": abort
"\C-x\C-g": abort
"\e\C-g": abort
"\C-j": accept-line
"\C-m": accept-line
# alias-expand-line (not bound)
# arrow-key-prefix (not bound)
# backward-byte (not bound)
"\C-b": backward-char
"\eOD": backward-char
"\e[D": backward-char
"\e!": complete-command
"\e/": complete-filename
"\e@": complete-hostname
"\e{": complete-into-braces
"\e~": complete-username
"\e$": complete-variable
# copy-backward-word (not bound)
# copy-forward-word (not bound)
# copy-region-as-kill (not bound)
....
....
41. touch /forcefsck
The above command will create an empty folder ‘forcefsck‘, under root directory. This will force Linux System to check the file system on the very next boot.
root@tecmint [~]# touch /forcefsck
That’s all for Now. You People are loving these ‘Lesser Known Commands‘ and hence we are continuing the series, the next article of this series will be available very soon.
Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to give your valuable feedback in our comment section. Do a favor to us, Like and share us and help us spread.



“35. Display Date on the Terminal”.
What is more tedious? Typing in 4 characters ‘DATE‘ and getting back the current date and time, or having to type in a series of intricate commands (susceptible to finger checks)? Yes, the string of commends can be saved as a script but then you still have to type in the name of the script on the terminal (more finger checks).
“38. host and dig Commands”
You explain what the ‘host’ command is used for. You don’t explain what the ‘dig’ command is used for.
“41. touch /forcefsck”
Maybe you should explain that the ‘touch’ command is used generally to create files/directories and then explain the specific ‘/forcefsck’ example.
34. getconf LONG_BIT
This produces no output on my system.
Hi tecmint team
I think you should post commands which used frequently in daily work :D
For example command number 37 :D
Thanks for your useful tutorial ^_^
Thanks @ quydo,
for your such valueable feedback.
All the commands are useful, at some point of time.
the linux command to reset your password for the currently logged user. plz tell me….
Run the ‘passwd username’ to command to reset current logged in user. Make sure you must be root user to perform such command.
Great List, Thanks.
Thanks @sam, for your nice feedback. Comment of such kind Encourages us :)
“job” command is not working in Centos-6.4, Any idea ?
Run jobs command, not job…