Just like any other operating system, Linux also supports a rich Graphical User interface (GUI). In fact, it supports multiple graphical desktop environments such as – GNOME, KDE, Cinnamon, and the list goes on.
However, most Linux administrators and power users prefer to use the command line interface, because it allows us to automate repetitive tasks using the scripts.
One of the trivial downsides of this approach is that often times the terminal gets filled up with the command’s or script’s output. So, in some cases, cleaning up the terminal becomes necessary.
In this guide, we will discuss various methods that allow us to clean up the Linux terminal. After following this guide, Linux users can use one of the methods while working with Linux’s command line interface.
Table of Contents
1. Clear Linux Terminal Using clear Command
The clear command is one of the most commonly used commands for clearing the Linux terminal. This command simply clears the terminal screen including its scroll-back buffers.
To understand the usage of the command, let’s execute a few commands in the terminal:
$ echo "Hello, World!" $ cat /etc/os-release
Now, to clean up the screen, just execute the clear command without any argument:
$ clear

2. Clear Linux Terminal Screen Using CTRL+L Shortcut
In a similar way, we can use the ctrl+L shortcut to clear the terminal screen. However, this method doesn’t clean up the scroll-back buffers.
To illustrate this, first clear the terminal screen using the ctrl+L shortcut and then scroll up the screen using the mouse:
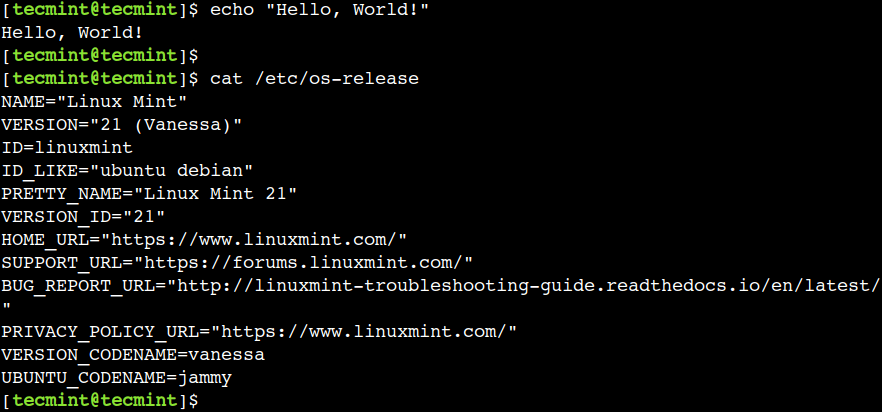
In this example, we can see the previous output by scrolling up the terminal.
3. Reset (Clear) Linux Terminal Using reset Command
Additionally, we can also use the reset command to clear the terminal screen. Just like the clear command the reset command also clears the scroll-back buffers.
The reset command reinitializes the terminal hence it takes more time compared to the clear command.
$ reset

4. Clear the Terminal Using the Escape Code
We can use the <ESC>c escape code to clear the terminal. Let’s understand with a simple example.
In bash, we can use the \e escape sequence to represent the ESC character. So, to clear the terminal screen we can use the \ec string with the printf command as shown below:
$ printf "\ec"
In a similar way, we can use the \033 octal number to represent the ESC character. So to clear the terminal, we can use the \033c string with the printf command:
$ printf "\033c"
In addition to this, the hexadecimal number \x1B represents the ESC character. Hence we can use it to clear the screen:
$ printf "\x1Bc"
In this guide, we discussed various methods for clearing the Linux terminal screen. Linux users can use one of the methods as per their choice.
Do you know of any other method for clearing the terminal in Linux? Let us know your views in the comments below.



In your example of using printf, shouldn’t “3c” read “\033c” ?